中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 843-847.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.06.004
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
血管基质成分联合脱细胞骨基质-壳聚糖支架修复桡骨缺损
邵擎东1,汪 铮2,李宇飞3,许天明1,孙久一1,江 峰1,吕峰霞1
- 解放军第四五五医院,1骨科,2生物诊疗科,3整形外科,上海市 200052
Stromal vascular fraction combined with acellular bone matrix-chitosan scaffold for radical defect repair
Shao Qing-dong1, Wang Zheng2, Li Yu-fei3, Xu Tian-ming1, Sun Jiu-yi1, Jiang Feng1, Lv Feng-xia1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 2Department of Biological Diagnosis and Treatment, 3Department of Plastic Surgery, the 455th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Shanghai 200052, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脱细胞骨基质:是将骨中的活细胞杀死,脂肪皂化,在降低骨抗原性的同时又保留骨的原有结构、力学性质而得到的具有良好生物、理化性能的骨组织工程支架材料,保留骨的天然特性。
壳聚糖:是由自然界广泛存在的几丁质(chitin)经过脱乙酰作用得到的,化学名称为聚葡萄糖胺(1-4)-2-氨基- B-D葡萄糖,自1859年,法国人Rouget首先得到壳聚糖后,这种天然高分子的生物官能性和相容性、血液相容性、安全性、微生物降解性等优良性能被各行各业广泛关注,在医药、食品、化工、化妆品、水处理、金属提取及回收、生化和生物医学工程等诸多领域的应用研究取得了重大进展。
背景:研究表明,复合使用人工组织工程骨材料和脱细胞骨基质做为骨缺损修复的支架材料,可以综合两者的优点。
目的:进一步验证脂肪组织基质血管基质性成分联合脱细胞骨基质壳聚糖支架复合物修复兔桡骨缺损的安全性和生物相容性。
方法:取38只新西兰大白兔,其中3只用于脂肪组织血管基质成分的制备,3只用于脱细胞骨基质的制备,32只分为实验组和对照组,采用Brownlow法制备桡骨缺损型,实验组移植血管基质成分-脱细胞骨基质壳聚糖复合支架,对照组造模后不做任何处理。术后2,4个月分别进行一般情况和大体观察、X射线拍照、病理观察、Lane-Sandhu 组织学评分。
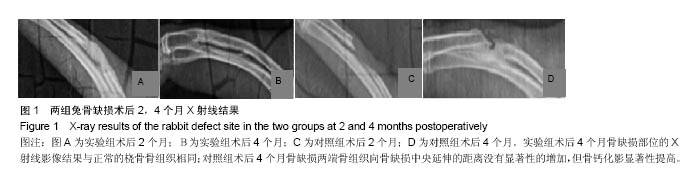
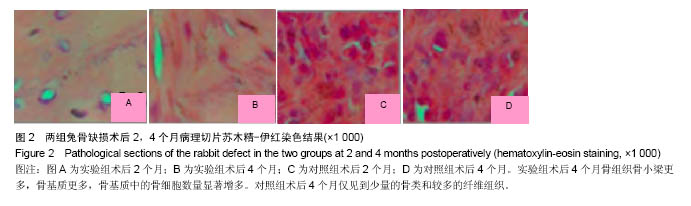
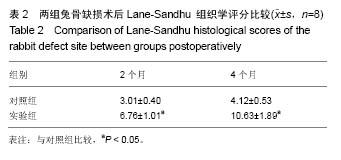
结果与结论:①术后2,4个月2组无感染现象,但实验组的活动量和愈合程度显著性好于对照组;②术后2个月实验组骨缺损部位的X射线影像结果有显著灰白色的高密度影,术后4个月与正常的桡骨骨组织相同,对照组骨不连接;③术后2,4个月实验组病理显示骨组织生长情况显著性的高于对照组,Lane-Sandhu 组织学评分显著性的高于对照组(P < 0.05);④结果说明,血管基质成分-脱细胞骨基质壳聚糖复合支架修复兔桡骨缺损具有很好的安全性和生物相容性。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)